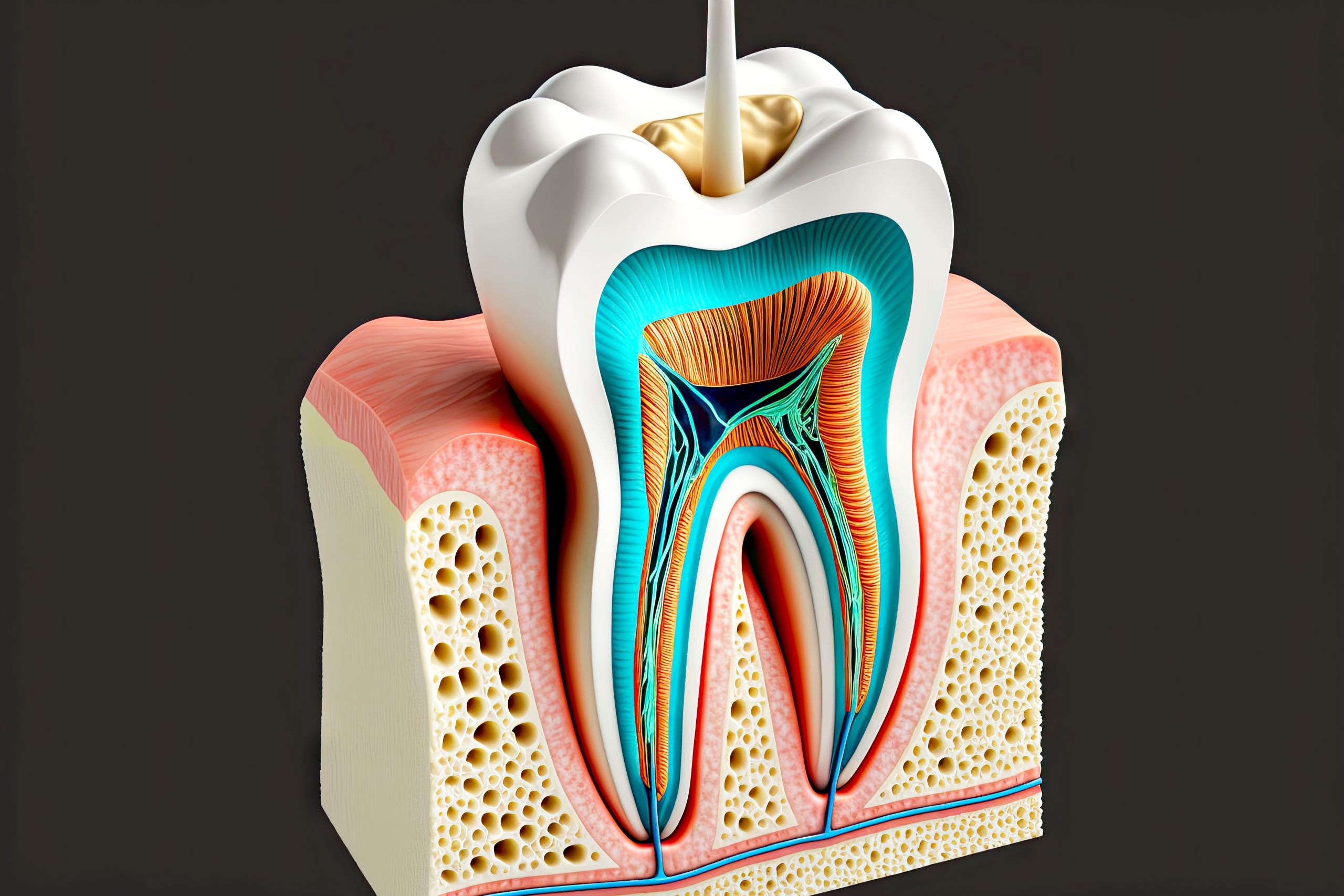
Sodium Hypochlorite Accidents in Endodontics: An Overview
Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) is the most commonly used irrigant in endodontic treatment due to its excellent antimicrobial and organic tissue dissolution properties. However, it is also known for its cytotoxic effects when extruded into the periapical tissues during endodontic treatment, resulting in the dreaded NaOCl accident. This blog post provides an overview of the various factors that can influence the occurrence and extent of NaOCl accidents.
- Patient-related Factors
Patient factors like age, gender, position on the dental chair, bone density, orthodontic treatment, immunocompromised status, and pulpal/periapical status can increase chances of NaOCl extrusion beyond the root apex. Younger patients and female patients are at higher risk.
- Tooth-related Factors
Tooth factors like root defects, open apex, proximity to maxillary sinus, and patency of apical foramen can provide easy passage for irrigant extrusion. Mandibular molars and maxillary premolars are more prone.
- Operator-related Factors
Operator inexperience, inappropriate anesthesia, access cavity errors, excessive apical enlargement, improper irrigation force and techniques like syringe irrigation can increase risks. Delayed referral and poor management can worsen prognosis.
- NaOCl-related Factors
Higher concentration, volume, pH and temperature of NaOCl can increase its tissue toxicity. Nature of contact, spread and duration of contact with tissues also play a role.
Conclusion
A combination of the above predisposing factors can lead to NaOCl accidents resulting in complications ranging from mild to severe tissue necrosis, airway obstruction or even death. Being aware of these risk factors, following irrigation protocols and early management is key to prevent and reduce the extent of such life-threatening complications.
Content summarized from:
Factors influencing the occurrence and progress of sodium hypochlorite accident: A narrative and update review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10003279/